Development and evaluation of a software system to harvest patient opinions about specific medical implants from social media sources
The increasing use of social media provides access to a wide range of information which was previously hard to collect. For implant manufacturers and other professionals within the field, the experiences and opinions of patients using implants are of great value.
Because patient reports in social media are not meant for automated processing and occur within a bigger set of data, special tools are required to find relevant texts and extract useful information.
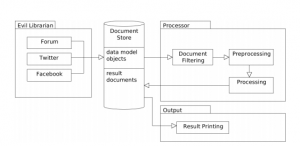
This work describes an extensible software framework which was implemented to approach the task. It collects documents form different social media sources and transforms them into a unified data model. The analysis consists of document filtering, preprocessing, simple methods like TF*IDF, inclusion of a sentiment analysis tool and statistical inspection.
Results show some of the difficulties that occur when processing free form texts. Examples show that, in order to retrieve meaningful results, manual steps are necessary. Strong trends in Twitter data can be seen with relatively little effort.x
