Finding causes – solving visual problems – ensuring better care
The web-based BTSO learning app offers an innovative and practice-orientated solution: a digital tool for simplified access to knowledge and tools. It teaches professionals how to recognise binocular abnormalities more quickly and how to treat them appropriately.
BTSO is a non-profit project that invests its income in further development, research and improvement.
Free trial phase for 4 weeks – immediately available with all functions but without data storage.
The paid version allows all data to be stored and is activated when you take part in a course (online or in person). Costs 33 CHF / month. The minimum term is one year.
Vision-related problems are common.
- 56% vision-related problems (e.g. headaches or tired eyes) of all patients aged between 18 and 38 years n= 1679 in five vision centers (Montés-Micó, 2001).
- 46% asthenopic problems in computer users n= 419 (Bhanderi, Choudhary, & Doshi, 2008).
Classification allows a targeted approach to solving the problems.
- 32% can potentially benefit from the classification
(García-Muñoz, Carbonell-Bonete, Cantó-Cerdán, & Cacho-Martínez, 2016), and (Hussaindeen et al., 2017).
Easy to get started with the minimal test battery (3 tests)
Detect vision problems and their causes quickly and easily: With just three measurements, it is possible to determine very specifically whether binocular vision or accommodation is abnormal. The BTSO learning app shows how a classification is made.
Schoolchildren can also be quickly screened for vision problems using the minimal test battery.
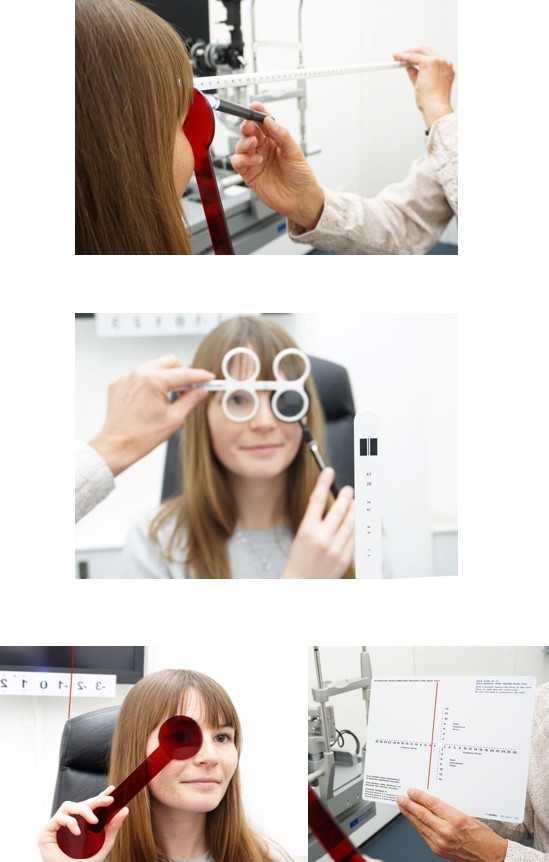


Monocular accommodation flexibility with +/- 2.0 dpt flipper
Difference between Maddox phoria / mod. Thorington card far-near
Features
- Quick and easy. The test sequence takes about 6 minutes, the evaluation 1-2 minutes.
- Can be used during the eye test or in quick mode after the eye test.
- Can be used from school age. User guidance through all steps of the measurements with information displays.
- Evaluation graphic to make all parameters visible at a glance and to show whether they are within the normal range or not based on their position.
Illustrations Graphic profile line
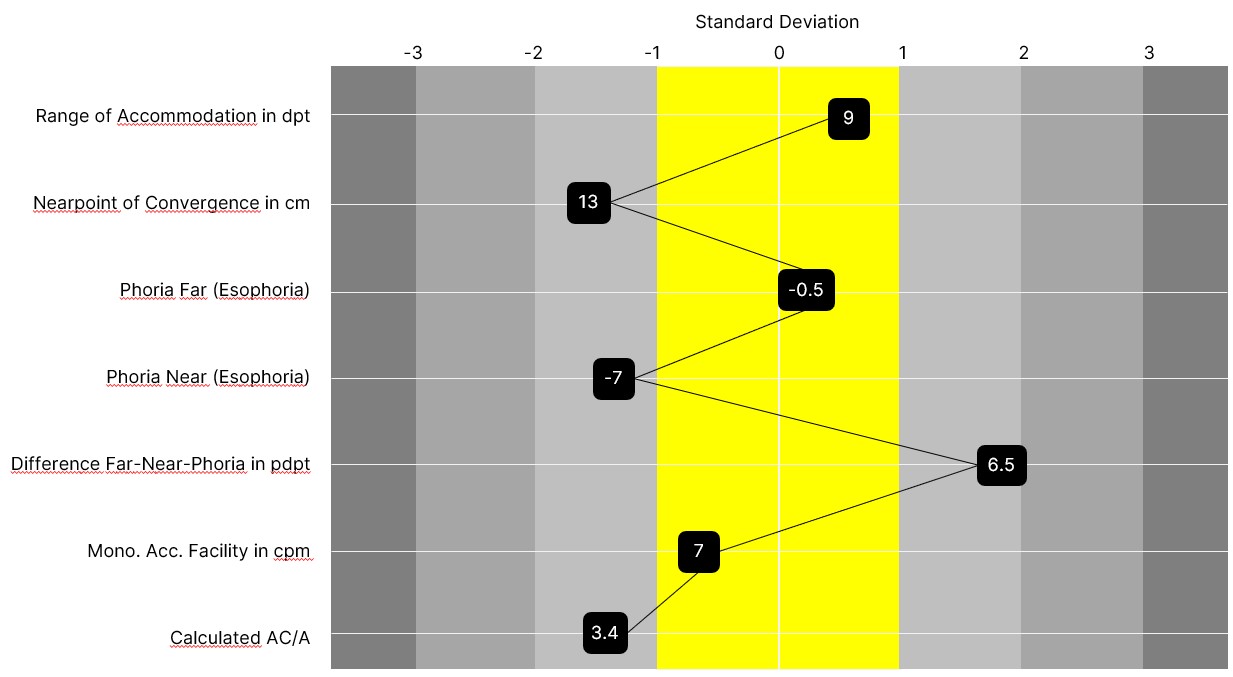
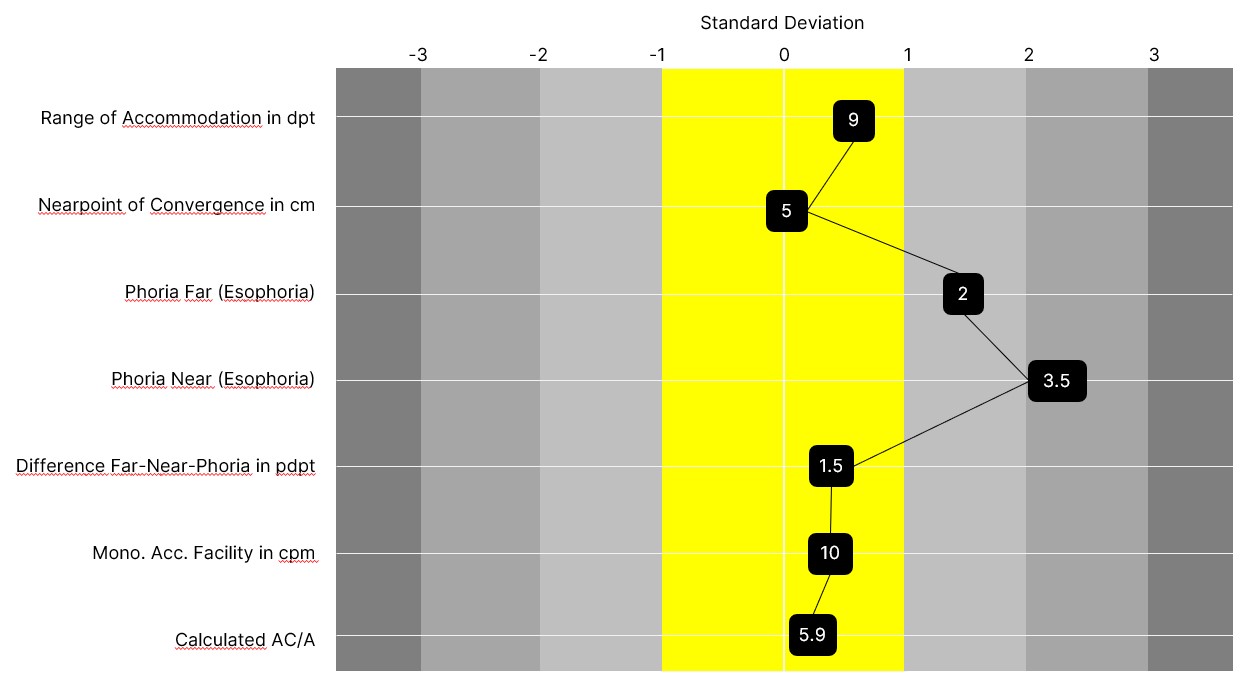
Basis esophoria