Characterisation of the monomeric archaeoeukaryotic Primase from Nanoarchaeum equitans
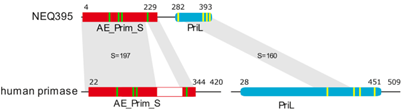
The marine thermophilic archaeon Nanoarchaeum equitans possesses a monomeric primase encompassing the conserved domains of the small catalytic and the large regulatory subunits of archaeoeukaryotic heterodimeric primases in one protein chain. The recombinant protein primes on templates containing a triplet with a central thymidine, thus displaying a pronounced sequence specificity typically observed with bacterial type primases only. The N. equitans primase (NEQ395) is a highly active primase enzyme synthesizing short RNA primers. Termination occurs preferentially at about nine nucleotides, as determined by HPLC analysis and confirmed with mass spectrometry. Possibly, the compact monomeric primase NEQ395 represents the minimal archaeoeukaryotic primase and could serve as a functional and structural model of the heterodimeric archaeoeukaryotic primases, whose study is hindered by engagement in protein assemblies and rather low activity (Schneider et al., 2023).
Funded by Schweizer Nationalfond.
Schneider, A., Bergsch, J., Lipps, G., 2023. The monomeric archaeal primase from Nanoarchaeum equitans harbours the features of heterodimeric archaeoeukaryotic primases and primes sequence-specifically. Nucleic Acids Res. gkad261. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkad261